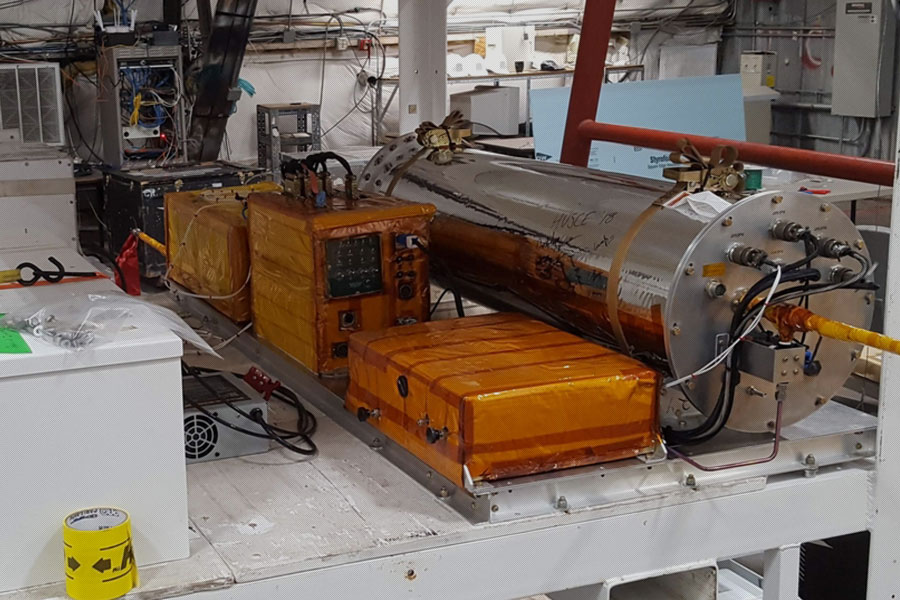
Above:
HUSCE payload mounted in a balloon gondola.
Harvard Collaboration
JPL Lasers Go to School
Siamak Forouhar - Jim Anderson
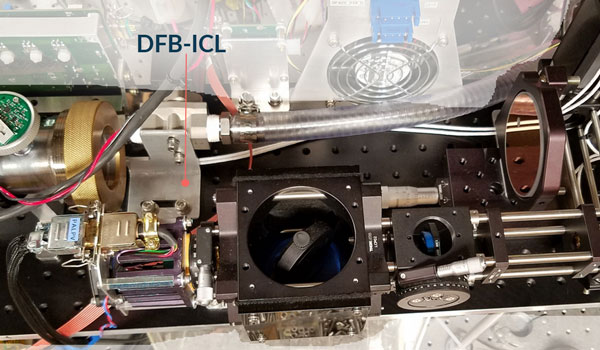
Harvard and JPL have been collaboratively pursuing the development of high power pulsed and CW laser systems for demanding spectroscopic applications since 2010. This partnership has resulted in two recent success stories. Harvard recently flew a laser developed as part of a NASA ACT grant on a NASA high-altitude research balloon. This was part of the NASA Undergraduate Student Instrument Project (USIP) program: it was a DFB-ICL (Distributed-Feedback Interband Cascade Laser), packaged with a thermoelectric cooler and integrated lens to produce a collimated beam in the 3.3 micron region. The flight profile included four hours of float time during which the balloon utilized controlled helium releases to step down between 96,000 and 50,000 ft. altitude. The laser and instrument performed well in this demanding thermal environment and successfully acquired measurements throughout the flight’s operational phase.
Harvard will also be flying JPL-produced lasers as part of the Water Isotopologues - Integrated Cavity Output Spectrometer (WI-ICOS instrument on the Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere (DCOTSS) mission that was selected as part of the 2017 NASA Earth Venture Suborbital-3 solicitation. These lasers will measure water vapor and total water isotopologues in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere on NASA's ER-2 research aircraft. The high power and integrated lens packaging design of these lasers in the 3 µm wavelength region represent a key advancement compared to commercially available state of the art, and are essential to facilitating WI-ICOS’s high-sensitivity approach to absorption spectroscopy.
JPL-produced DFB-ICL integrated in optical train for HCl instrument that flew as part of HUSCE.
+ Larger image
The WI-ICOS instrument that will be part of DCOTSS. The black enclosure at the bottom of the picture is the laser pressure vessel that houses the JPL-developed laser.
+ Larger image