Above:
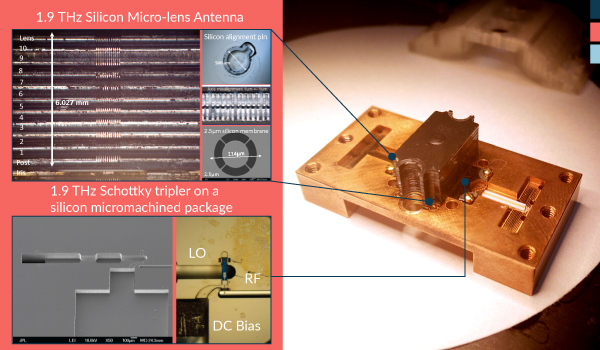
1.9 THz silicon micro-lens antenna.
Small Lenses
Small Lenses for a Big World
Maria Alonso - Cecile Jung-Kubiak - Goutam Chattopadhyay
The antenna used to couple the radiation to the sensor is a key component to ensure that the system achieves the sensitivity to perform the scientific observations. In this effort, we have designed a waveguide-based antenna that is fully compatible with silicon micromachining processes and has a performance that is greater than the traditional metal-machined horns at these frequencies. The antenna geometry consists of a waveguide feed, which excites a silicon lens antenna through an Electromagnetic Band-Gap (EBG) resonant cavity that contains a 2.5um silicon membrane iris.
This membrane+cavity is used to match the waveguide feed with the silicon medium as well as to illuminate the upper part of the lens. One of the key features of this novel antenna is that we do not need to fabricate the full silicon elliptical lens, instead, only a small part of the lens needs to be fabricated. MDL has developed a process to fabricate micro and millimeter-size shallow lenses using photolithographic processes.
Overall, by having successfully develop this full Schottky based source and antenna using silicon micromachining processes, we can envision a clear path to make multiple pixel arrays on a single wafer integration.
A 1.9 THz micro-lens antenna has been fabricated and demonstrated providing radiation from a multiplied source. The micro-lens is fabricated by utilizing gray scale masks and deep reactive ion etching.
+ Larger image